 As expected, the decision to mandate the shutdown of a large segment of the U.S. economy in efforts to reduce the spread of the coronavirus delivered record acceleration in the rate of unemployment. Just two months ago, payrolls increased by 230,000 jobs and unemployment fell back to a half century low of 3.5%.
As expected, the decision to mandate the shutdown of a large segment of the U.S. economy in efforts to reduce the spread of the coronavirus delivered record acceleration in the rate of unemployment. Just two months ago, payrolls increased by 230,000 jobs and unemployment fell back to a half century low of 3.5%.
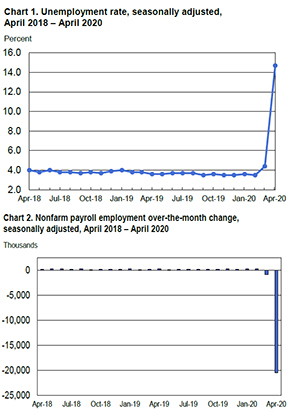
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reported the unemployment rate increased by 10.3 percentage points to 14.7%. That is the highest rate and the largest month-over-month increase in the history of the series dating back to 1948. Total number of unemployed persons increased by an astonishing 15.9 million to 23.9 million in April.
“The job losses and high unemployment mark a sharp pivot from just a few months ago, when the economy was pumping out hundreds of thousands of new jobs, and joblessness was hovering near 50-year lows. The jobs bust has been widespread,” noted the Wall Street Journal in an article issued shortly before April results were announced. Economists, meanwhile, had forecast an unemployment rate of 16% from 4.4% in March.
The stock market reaction at today’s opening, indicate that investors have already baked these numbers into their forecasts and have weighed anticipated steps in lifting restrictions.
“The jobs report marks a sobering moment in our history, while it also likely marks the bottom of the economic contraction with hope for a better remainder of the year,” said Bryce Doty, senior portfolio manager at Sit Fixed income Advisors, in a Bloomberg report.
Unemployment increases were widespread throughout the industries reported by the BLS. Roles in leisure and hospitality plummeted by 7.7 million, or 47 percent with almost three-quarters of the decrease in food services and drinking places (-5.5 million).
As the healthcare industry shifted to coronavirus mitigation the BLS data indicated that the remaining sectors in healthcare saw a decline by 1.4 million led by losses in offices of dentists (-503,000), offices of physicians (-243,000) and in offices of other healthcare practitioners (-205,000). There were declines too in professional and business services, construction, manufacturing, transportation and warehousing and in the financial sector among a broad range of industry declines.
In April, employment in retail trade declined by 2.1 million. Job losses occurred in clothing and accessories stores (-704,000), motor vehicle sales (-382,000) and furniture and home furnishing stores (-209,000). By contrast, the component of general merchandise stores that include warehouse clubs and superstores, that were largely unaffected by mandated closure gained 93,000 jobs.
Total government employment dropped by 980,000 in April with employment in local government down by 801,000 in part reflecting school closures according to the BLS.
Reported by CNBC, “The bleak numbers paint a pretty dismal picture, but April may be it for job losses going forward with the country starting to reopen,” said Chris Rupkey, chief financial economist at MUFG Union Bank. “If there is a silver-lining in today’s dismal jobs report, it is in the realization that the economy cannot possibly get any worse than it is right now.”

Connect with MRINetwork